Review of Radar Science, Technology, Applications, News, Publications, Industry, History, etc.
Wednesday, November 28, 2012
Thursday, November 22, 2012
Thales naval radars at IndoDefence 2012
Thales is at the forefront of developing new naval solutions to meet evolving environmental and security challenges. The Group has been a long-term partner for more than 50 Navies worldwide, providing customers with innovating offerings, from system design to through-life support. At IndoDefence 2012, Thales was showcasing its SMART-S Mk2 and VARIANT radars. Both types are already selected by the Indonesian Navy.
Albert Willemsen, Regional Export Marketing & Sales Director Asia,
presents the Thales Naval Radars on display during Indodefence 2012
SMART-S Mk2 Link to Thales Smart-S Mk2 datasheet
Smart-S Mk2 is the continuous evolution of Thales proven 3D multi-beam radar family. This radar operates in E/F-band (or S-band) and is optimised for surveillance of 250 km with 70º elevation overage, target designation and undisturbed air and surface target tracking in littoral environments. Development of Smart-S Mk2 started in 2003 and at present no less than 40 systems have been sold. Smart-S Mk2 matches the full performance envelope of modern surface-to-air missiles, with direct assignment of VL-MICA, Evolved Sea Sparrow Missile (ESSM) and is suitable as a main air and surface surveillance radar for corvettes, frigates and amphibious ships. The radar offers two main modes, a special helicopter/UAS guidance capability and three surface fire control channels.
The SMART-S Mk2 has been selected to equip the future Indonesian Navy corvettes KPR. It has also been selected to upgrade the existing French Navy Cassard class Anti-Aircraft Frigates.
Thales VARIANT radar is currently in use by the Indonesian Navy as well as 8 other navies worldwide (Picture: Thales)
VARIANT
Variant is a multipurpose, short/medium range (70 km) 2D radar, simultaneously operating in the X and C-band for air and surface surveillance. Its principal role is as an automatic, fast reaction time radar sensor supplying targeting data to weapon systems. Its extensive features make Variant the answer in modern warfare, littoral and asymmetric threat environments. Variant provides air tracks without any operator intervention (auto target initiation and tracking). For surface targets, two fire control channels are available to support direct target engagement. The system is completed by an integrated Low Probability of Intercept (LPI) surface surveillance radar (SCOUT).
VARIANT has also been selected by the Indonesian Navy and is currently deployed onboard their Todak class Fast Patrol Boat
Many Thales systems will be onboard the future Indonesian Navy SIGMA PKR 10514 (Picture: Damen Schelde Naval Shipbuilding)
The Shipyard Royal Schelde and Thales deliver a wide range of products on the two corvettes that Royal Schelde has built for the Indonesian Navy. Thales supplies the ship's above-water defence system, the communication equipment and the sonar system. The first ship was commissioned in 2007. The corvettes are deployed by the Indonesian Navy chiefly for patrol duties in the Indonesian archipelago in order to combat smuggling, illegal fishery and piracy, especially in the Strait of Malacca. The above water defence systems installed on the corvettes, include: the TACTICOS, scaleable combat management system, the MW08 3D multiband surveillance radar, the LIROD Mk2 tracking radar, the LINK Y Mk2 datalink system and Target Designation Sights. For under water defence capability, the Thales Kingklip medium frequency active/passive Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) hull-mounted sonar has been selected. The corvettes' naval communication systems have been developed by Thales, based on the FOCON system. Thales has integrated the complete combat system on these corvettes.
Wednesday, October 24, 2012
"Космонавт Юрий Гагарин" в море.
“Космонавт Юрий Гагарин” — научно-исследовательское судно, флагман судов Службы космических исследований СССР. Построено на Балтийском судостроительном заводе в Ленинграде в 1971 году. Длина одиннадцатипалубного теплохода 231,6 м, ширина 32 м, мощность главного двигателя 14 000 кВт, скорость хода 18 узлов, водоизмещение 45 000 т. Экипаж 136 чел., состав экспедиции 212 чел. На борту 1250 помещений, в т.ч. 86 лабораторий. Было предназначено для решения задач управления и связи одновременно с несколькими КА и Центром управления полетом через КА «Молния». На борту судна 75 антенн, в т.ч. две антенны с параболическими отражателями диаметром 25 м. Судно могло находится в автономном плавании в течение 130 суток. Район работы – Атлантический океан.
Saturday, September 22, 2012
SABR AESA Radar for the F-16
Northrop Grumman's Scalable Agile Beam Radar (SABR), designed specifically for the F-16, is the newest addition to the Northrop Grumman robust family of multi-function sensors. By leveraging Northrop Grumman's world-leading Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) technology base, SABR maximizes radar system performance within existing F-16 allocations. SABR has been chosen for the F-16 AESA upgrade program.
Friday, September 7, 2012
Wednesday, August 8, 2012
Saturday, July 28, 2012
Thursday, July 26, 2012
Cassidian announces passive radar system
Cassidian, the German defense and security division of EADS, is in the news with development of a stealth radar system.
It said its "passive radar" system can not only locate difficult-to-detect stealth aircraft, the system itself is practically undetectable since it doesn't emit radiation. Instead, it analyses radiation reflections from other emitters, such as radio and television stations, to detect objects.
"The principle of passive radar has been known for a long time," says Elmar Compans, head of Sensors and Electronic Warfare at Cassidian. "However, we have now integrated the latest capabilities of digital receiver and signal processing technology to significantly enhance range and detection accuracy by monitoring various emitters at the same time."
Cassidian said its passive radar meets the requirements of civil and military airspace control, which couldn't be fully met with standard emitting radar: In civil application, passive radar makes cost-effective air traffic control possible without any additional emissions and without demands on transmission frequencies; in military applications, it provides large-area surveillance using networked receivers but cannot be located by hostile forces.
"The particular characteristics of the omnipresent radio signals used for operation enable detection of even objects that are difficult to detect, such as stealth aircraft or stealth ships," Cassidian said.
"A further advantage of the new technology is its increased detection capacity in areas of radar shadow such as mountainous terrain and its capability to locate extremely slow and low flying objects."
The system is also mobile. It can be deployed in a vehicle of the size of a commercial van.
Testing of the system, including at Stuttgart Airport, has proved successful and a production prototype system will be manufactured for evaluation program by Cassidian and its customers by the end of the year.
A demonstrator passive radar system has been delivered to the German Federal Office of Defense Technology and Procurement, the company said.
In other Cassidian developments, the reported its Barracuda unmanned aerial system has completed a series of test flights at a military airfield in Canada.
Five tests were conducted this month and last and involved the Barracuda demonstrator flying in combination with a modified Lear jet to simulate another unmanned aerial vehicle.
In the tests the two aircraft flew missions where they each had different role profiles that were autonomously coordinated and synchronized with each other.
Cassidian said that coordination between the two aircraft was mostly automated but missions could be adapted by uploading new mission data while the aircraft were in the mission zone through the use of a new network-centric data link.
Flight test engineers transmitted new individual waypoints to the aircraft as well as entire mission segments from the ground station to the UAS in flight.
"With these latest successful flights by our UAS technology demonstrator, we have made another great leap forward in our developments for the world's most promising future markets in our industry," said Cassidian Chief Executive Officer Stefan Zoller.
The Barracuda demonstrator was designed as a technology test bed. It has a modular structure, enabling a variety of systems and flight profiles to be tested and a wide range of mission requirements to be demonstrated.
Its avionics system was also developed as an open and modular structure, the company said.
Thursday, July 19, 2012
Lifting the Fog: A Brief History of Radar
One of the worst airplane disasters in history occurred as a consequence of a series of unfortunate events. The location of the disaster was the island of Tenerife, the largest and most populated island of the Canary Islands, on March 27th, 1977. Two Boeing 747 planes prepared for departure on a crowded runway where they were instructed to follow a procedure called “backtaxi” where a portion of the runway is used as a taxiway for aircraft to taxi in the opposite direction from which they will take off. Through a series of misinterpreted communications between air traffic controllers and the pilots, one of the planes began their take off before the other, backtaxiing plane had cleared the same runway. Dense fog shrouded the planes from sight and they did not realize that they were barreling towards disaster until they were 2,000 feet from each other. A detailed account of the events of this fateful day can be found here.
Computer rendering of the Tenerife disaster. Source: http://www.nycaviation.com
Of all the events that led up to the disaster, the straw that broke the camel’s back was a dense layer of fog that clouded the two planes from each others', and the air traffic controller’s, vision. Unfortunately, the small airport on Tenerife was not equipped with ground-based radar, a tool that would have allowed the controllers to see the location of the planes even with the heavy cover of fog. Although this disaster happened 35 years ago, ground-based radar technology was already available, in fact, this technology was developed long before 1977.
Friday, July 6, 2012
‘Spy’ Radar Arrays Arrive in Adelaide
AN/SPY-1D(V) phased array radar for Hobart Class Air Warfare Destroyers (all photos : Lockheed Martin)
Minister for Defence Materiel Jason Clare announced the arrival in Adelaide of the first two state of the art ‘SPY’ radar array faces that will be installed on the Air Warfare Destroyers (AWDs).
“The multi-function SPY radar is capable of search, automatic detection, tracking of air and surface targets and missile engagement support,” Mr Clare said.
“It works to distinguish signals from stationary or moving targets and to identify and reject ‘clutter’ such as clouds and flocks of birds.”
Wednesday, June 27, 2012
Objective Optimization of Weather Radar Networks for Low-Level Coverage Using a Genetic Algorithm
James M. Kurdzo and Robert D. Palmer, 2012: Objective Optimization of Weather Radar Networks for Low-Level Coverage Using a Genetic Algorithm. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 29, 807–821. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1175/JTECH-D-11-00076.1
The current Weather Surveillance Radar-1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) radar network is approaching 20 years of age, leading researchers to begin exploring new opportunities for a next-generation network in the United States. With a vast list of requirements for a new weather radar network, research has provided various approaches to the design and fabrication of such a network. Additionally, new weather radar networks in other countries, as well as networks on smaller scales, must balance a large number of variables in order to operate in the most effective way possible. To offer network designers an objective analysis tool for such decisions, a coverage optimization technique, utilizing a genetic algorithm with a focus on low-level coverage, is presented. Optimization is achieved using a variety of variables and methods, including the use of climatology, population density, and attenuation due to average precipitation conditions. A method to account for terrain blockage in mountainous regions is also presented. Various combinations of multifrequency radar networks are explored, and results are presented in the form of a coverage-based cost–benefit analysis, with considerations for total network
Saturday, June 23, 2012
Realities of Rearmament
RIA Novosti yesterday quoted a VVKO spokesman who indicated a second battery of Pantsir-S anti-aircraft gun-missile systems will go into service this fall around Moscow. For the record, he stated:
“At present, alongside an A-150 missile defense [PRO] division, two S-400 anti-aircraft missile regiments in two-battalion configurations, deployed in Elektrostal and Dmitrov, provide Moscow with anti-air and anti-missile defense. One of them already has a ’Pantsir-S’ battery in its composition, in September-October, the second regiment will also receive the same battery complement.”
The spokesman added that, in August, the new Pantsir-S battery, along with its S-400 regiment at Dmitrov, will be in Ashuluk to perform ‘test’ live firings against low-altitude targets.

Novosti has some video of the Pantsir as does a background piece by Arms-Expo.ru.
Let’s add things up as best we can.
First Deputy Defense Minister Sukhorukov has said the army will get 28 Pantsir-S systems in 2012. The VVS CINC said there would be two more S-400 regiments (for a total of four) before the end of 2011. But, there are, as the VVKO spokesman says, still only two. The CINC also said the next six Pantsir-S systems would be for the Moscow area. The first four went to Novorossiysk.
Recall there was some question whether ten delivered in 2010 were for Russian forces or some foreign customer.
Thursday, June 7, 2012
An Extended Kalman Filter Framework for Polarimetric X-Band Weather Radar Data Processing
Marc Schneebeli and Alexis Berne, 2012: An Extended Kalman Filter Framework for Polarimetric X-Band Weather Radar Data Processing. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 29, 711–730. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1175/JTECH-D-10-05053.1
Abstract The different quantities measured by dual-polarization radar systems are closely linked to each other. An extended Kalman filter framework is proposed in order to make use of constraints on individual radar observables that are induced by these relations. This new approach simultaneously estimates the specific differential phase on propagation Kdp, the attenuation-corrected reflectivity at horizontal polarization Zh, and the attenuation-corrected differential reflectivity Zdr, as well as the differential phase shift on backscatter δhυ. In a simulation experiment it is found that Kdp and δhυ can be retrieved with higher accuracy and spatial resolution than existing estimators that solely rely on a smoothed measurement of the differential phase shift Ψdp. Attenuation-corrected Zh was retrieved with an accuracy similar to standard algorithms, but improvements were found for attenuation-corrected Zdr. In addition, the algorithm can be used for radar calibration by comparing the directly retrieved differential phase shift on propagation Φdp with the accumulated Kdp estimates. The extended Kalman filter estimation scheme was applied to data collected with an X-band polarimetric radar in the Swiss Alps in 2010. Radome attenuation appears to be significant (up to 5 dB) in moderate to intense rain events and hence needs to be corrected in order to have reliable quantitative precipitation estimates. Measurements corrected for radome and propagation attenuation were converted into rain-rate R with a newly developed relation between R, Kdp, and Zdr. The good agreement between rain-rate values inferred from ground observations and from the radar measurements confirms the reliability of the proposed radar processing technique.
Tuesday, May 15, 2012
Saturday, April 28, 2012
Что такое СПРН России?
СПРН России - Российская система предупреждения о ракетном нападении. Ее основной задачей является обнаружение ракетной атаки в момент пуска и передача данных об атаке системе противоракетной обороны. Оперируя полученными от СПРН сведениями о масштабе и источнике атаки, оборонные системы рассчитывают варианты ответных действий. СПРН состоит из наземных радиолокационных станций с дальностью обнаружения 6 000 км и группы орбитальных спутников, способных обнаруживать запуск межконтинентальных ракет из любой точки планеты.
Разработка СПРН в России началась в середине ХХ века, в разгар холодной войны между Америкой и Советским Союзом. Всплеск научных разработок в области ядерного оружия привел к появлению межконтинентальных баллистических ракет, и, как следствие, возник вопрос об эффективном противодействии в сфере ПВО. В 1954 году начались работы по созданию радиолокационной станции дальнего обнаружения.
Первые РЛС раннего предупреждения были развернуты в конце 60-х годов по периметру границы Советского Союза. Их задачей было обнаружение запущенных ракет и их головных частей, а также вычисление координат местонахождения ракет в реальном времени с максимальной точностью, определения района падения и прогноз предполагаемых масштабов разрушения. После успешно проведенных испытаний была создана единая система предупреждения о ракетном нападении, объединившая отдельные радиолокационные станции, узлы, комплексы и командные пункты управления, размещенные на территории СССР.
Наряду с этим шла работа над программой создания космической составляющей СПРН. В 1961 году к рассмотрению был представлен проект системы космического наблюдения, и в 1972 году после ряда испытаний и доработок на орбиту был выведен спутник, оснащенный приборами обнаружения инфракрасного и телевизионного типа.
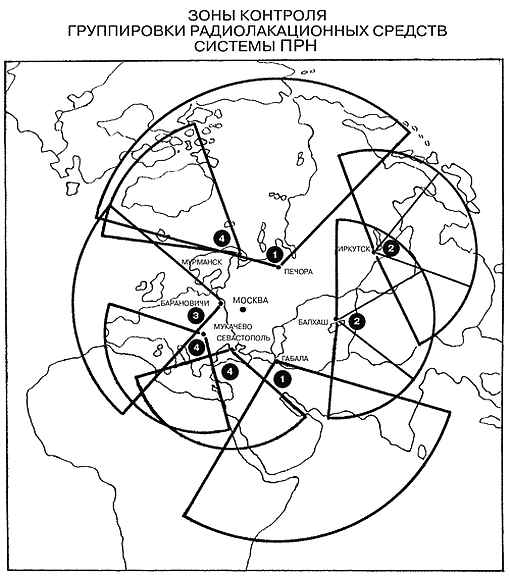
Таким образом в 1972 году система состояла из наземных надгоризонтных и загоризонтных РЛС и космических спутников СПРН, чьей задачей было регистрировать запуски баллистических ракет. Инфракрасные датчики, размещенные на спутниках, должны были улавливать излучения выхлопов ракетного двигателя во время прохождения активного участка траектории. Загоризонтные РЛС, размещенные на территории СССР, могли регистрировать сигнал ракетного пуска в США, принимая отражение этого сигнала через ионосферу. РЛС надгоризонтного типа обнаруживали боевые части ракет при прохождении более поздних участков баллистической траектории.
Thursday, April 5, 2012
Ми-28Н с модифицированной РЛС
Новейшая фотография известного боевого вертолета Ми-28Н (бортовой номер "36 желтый", серийный номер 01-05, заводской номер 34012835105), используемого ОАО "Московский вертолётный завод имени М.Л. Миля" для отработки бортовой РЛС Н025 в надвтулочном обтекателе. Данный борт стал первым экземпляром вертолета Ми-28Н, получившем РЛС Н025, начав испытательные полеты с ней в феврале 2007 года. На данной фотографии, сделанной 2 апреля 2012 года, заметно, что обтекатель антенны РЛС несколько отличается деталями от ранее использовавшегося, что заставляет сделать вывод о начале испытаний доработанного варианта РЛС Н025.

Ми-28Н (бортовой номер "36 желтый", серийный номер 01-05, заводской номер 34012835105) с модифицированной РЛС Н025. Панки, 02.04.2012 (с) kabuki/russianplanes.net
Friday, March 30, 2012
Thursday, March 29, 2012
Wednesday, March 28, 2012
Saturday, March 24, 2012
PAVE PAWS - On a cloudy day…
Monday, March 5, 2012
Прошлое и будущее "Дарьяла"
Россия хочет продлить срок аренды РЛС «Дарьял» до 2025 года.

РЛС «Дарьял», ещё известная как отдельный радиотехнический узел космических войск РФ, Габала-2, РО-7, объект 754, была построена в 1985 году на севере Азербайджана, неподалёку от города Габала, одна из девяти станций данного типа. Цель постройки - предупреждение ракетного нападения на Советский Союз с южного направления. Возможно обнаружение пусков наземных и морских баллистических ракет, способных нести ядерные боеголовки, а также для непрерывного контроля космического пространства. Радар охватывает Иран, Турцию, Ближний Восток, Пакистан, Индию. Радиус обнаружения станции, по разным данным, составляет 6-8 тыс.км. Потребляемая станцией мощность не превышает 50 МВт. Штатная численность обслуживающего персонала РЛС (по состоянию на 2007 год) составляет около 900 военнослужащих и 200 гражданских специалистов.
Sunday, March 4, 2012
Монолит-Б – береговой комплекс разведки воздушной и надводной обстановки
Комплекс предназначается для загоризонтного обнаружения воздушных и надводных объектов и сопровождения обнаруженных объектов.
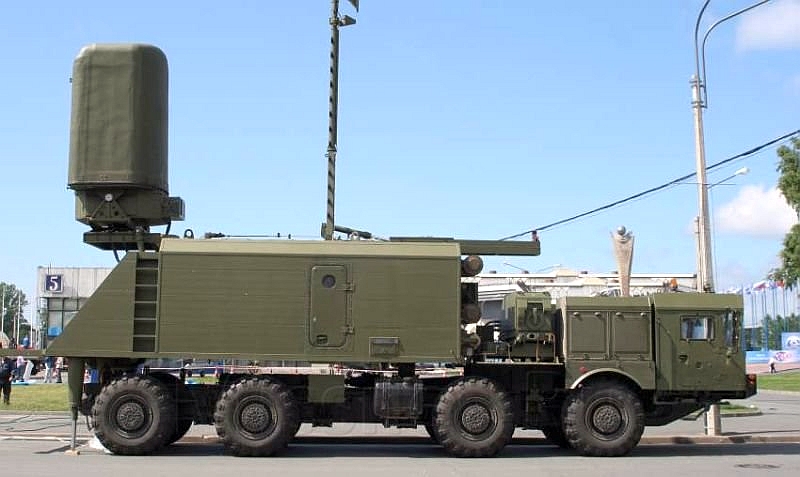

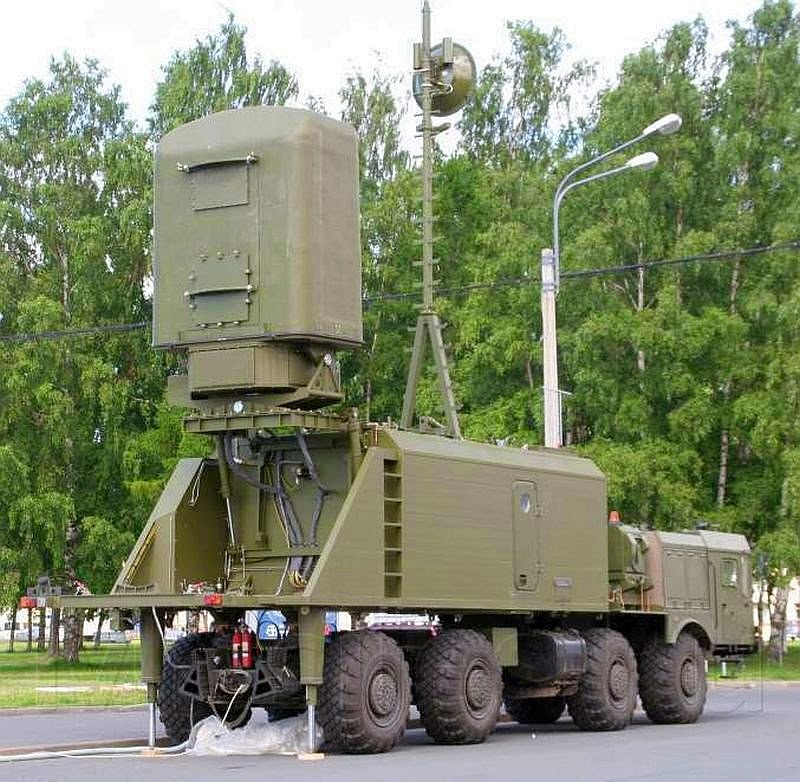
Для этого используются собственные средства активно-пассивной радиолокации, автоматизированные прием и обработка данных о надводно-воздушной обстановке. Данные снимаются с носителей изделий «Минерал-МЭ», спецаппаратуры сопряжения и от других источников получения данных – НП, вертолетов и кораблей. Данные снимаются по обычным линиям связи. Также комплекс используется для обработки и выдачи информации целеуказания системам управления ракетным вооружением береговых ракетных комплексов. Комплекс создан на шасси МЗКТ-7930. Основной разработчик - ОАО «Тайфун».

Комплекс способен обнаружить до 50 объектов по горизонту на дальности до 250 километров в пассивном режиме и 450 км в активном режиме радиолокации. В пассивном режиме сопровождается 10 обнаруженных объектов, в активном - более 30 объектов. Основные получатели целеуказания – ПБРК «Бастион» и ПБКРО «Клаб-М». Комплекс был представлен на международном военно-морском салоне «МВМС-2011», прошедшем в Санкт-Петербурге.

Thursday, March 1, 2012
Генерал Ивашов: Мы проиграли Габалу
Россия, видимо, потеряет радиолокационную станцию (РЛС) «Дарьял» в Габале. Переговоры Москвы и Баку о продлении договора «О статусе, принципах и условиях использования Габалинской РЛС» зашли в тупик. Об этом сообщает «Коммерсант». Азербайджан формально не разрывает договоренностей, просто с 2012 года хочет получать за аренду станции вместо нынешних 7 млн долларов в год фантастические 300 млн долларов.
Момент для торга выбран неслучайно. В нынешнем году истекает десятилетний срок действия соглашения между РФ и Азербайджаном об использовании РЛС «Дарьял». Соглашение автоматически пролонгируется на три года, если ни одна из сторон за полгода до истечения срока действия документа не уведомит другую о намерении его расторгнуть (пограничные полгода истекают 9 июня 2012-го).
Получается, России нужно либо платить 300 млн долларов в год, либо уходить из Габалы. Этот уход чреват проблемами. По идее, «Дарьял» способна заменить новая РЛС в Армавире – «Воронеж-ДМ». Но пока она не способна отслеживать ракетные пуски в зоне ответственности Габалы, поскольку соответствующее оборудование только предстоит вводить в строй. Кроме того, свято место пусто не бывает – едва Россия свернет РЛС в Габале, на ее месте мигом появится РЛС «конкурентов» – Турции или США (она очень пригодится партнерам по НАТО в случае конфликта с Ираном).
Впрочем, есть другой путь решения конфликта по Габале – уступки России в газовой сфере. Не нужно быть семи пядей во лбу, чтобы понять, за что мстит Баку.
Во-первых, Москва блокирует строительство Транскаспийского газопровода в обход РФ. Ветка должна пройти по дну Каспийского моря и транспортировать 20-30 млрд кубов газа в год из Туркмении прямиком в газопровод Nabucco – конкурента газпромовского South Stream. Москва же считает, что юридически статус Каспийского моря не определен, дно не разграничено, и без согласия всех прибрежных стран Баку и Ашхабад не имеют права прокладывать газопровод.
Во-вторых, Россия положила глаз на азербайджанское газовое месторождение Шах-Дениз на Каспии. В 2010-м году «Газпром» предложил выкупить весь свободный объем азербайджанского газа, но Баку предложение отверг.
Уйдет ли Россия из Габалы, или поступится экономическими интересами, рассуждает президент Академии геополитических проблем, генерал-полковник Леонид Ивашов.
Saturday, February 18, 2012
Мобильная РЛС 64Л6 "Гамма-С1"
64Л6 «Гамма-С1» является 3-х координатной, сантиметрового диапазона РЛС обзорного типа. Данная РЛС была построена на смену комплекса дальномер-высотомера с радиолокационной станцией П-37, и высотомерами ПРВ – (13/16). Создание мобильной Гаммы-С1 поручили Горьковскому НИИРТ. Согласно проекта, РЛС должна была использоваться как станция БР межвидового применения в подразделениях противовоздушной обороны и войсках ВВС. При создании мобильной РЛС образец станции участвовал в ходе проведения учений ПВО. На защиту отечества «Гамма-С1» поступает в 2003 году, РЛС пошла в серийное производство. Изготавливают «Гамма-С1» на Муромском заводе радиоизмерительной аппаратуры. В производстве участвуют ОАО «ПЗРА» и «ВНИИРТ». Опытную эксплуатацию РЛС 64Л6 успешно прошла в Московском подразделении РТВ. Конструкторы заложили в радиолокационную станцию большой запас для модернизации. Некоторые источники в 90 годах называли данную РЛС -96Н6Е «Гамма-С1Е». По результатам проведенных испытаний до серийного выпуска РЛС показала, что она полностью соответствует заданным характеристикам:
- обнаруживает и измеряет три координаты воздушных объектов;
- быстро определяет государственную принадлежность обнаруженных объектов;
- точно распознает цели по классу;
- определяет угломерные и азимутальные пеленги на объекты активных помех;
- выдает цифровую информацию на приборы отображения информации.
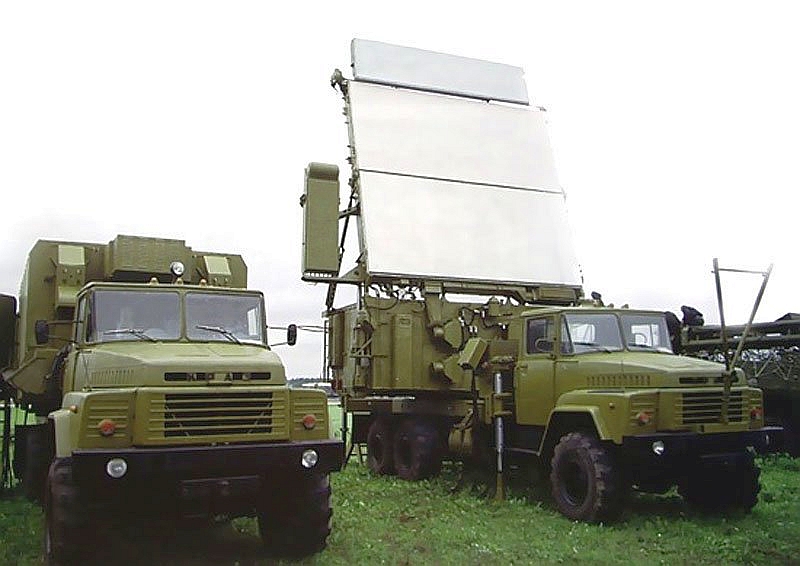

Антенная составляющая РЛС установлена на автомашине М-1 и является плоской фазированной антенной решеткой (ФАР), которая выполняет электронное сканирование приемо-передающих лучей по диаграмме направленности в вертикальной плоскости. Реализация последовательного обзора позволяет РЛС контролировать программным методом излучаемую энергию. В передающем устройстве используется современный российский электровакуумный прибор – широкополосный многолучевой клистрон, обладающий большой выходной мощностью и высокой степенью надежности. По основным характеристикам не уступает лучшим мировым аналогам. Вся аппаратура «Гамма-С1» обладает высокой автоматизацией обнаружения воздушных объектов и выбора режима работы. Режим работы выбирается, исходя из обработанных данных обстановки оператором или автоматически.
Thursday, February 2, 2012
Lockheed Martin - Air and Missile Defense Radar S-Band (AMDR-S) Digital Array Radar
Lockheed Martin selected to demonstrate designs for next phase of Navy's Air and Missile Defense Radar program.
A $119 million U.S. Navy contract, awarded Sept. 30, advances Lockheed Martin another step in the Navy's competition for the next generation naval radar system capable of defeating anti-ship and ballistic missile threats.
Currently, the Navy's Air and Missile Defense Radar (AMDR) program is focused on developing and demonstrating an entirely new S-band radar and a scalable radar suite controller for multiple ship platforms, performing multiple missions, in the Fleet. The Navy began its AMDR program by awarding Lockheed Martin and two other contractors concept studies contracts in 2009. This new contract begins a 24-month technology demonstration phase, where Lockheed Martin and three other competitors now will show the Navy how their conceptual designs actually work.
"AMDR is an important program for Lockheed Martin and we are look forward to executing the technology demonstration phase contract. Our high performance radar suite is capable of supporting simultaneous, multi-mission operations in stressing environments while maintaining affordable lifecycle costs," said Carl Bannar, vice president of Radar Systems. "Our modular, open-architecture design for AMDR incorporates technologies matured through significant investment by our company and the Navy."
Lockheed Martin is a leader in S-band radar development and production, with more than 40 years of experience in the design, production and sustainment of naval radars for surface combatants. The company's SPY-1 family of radars -- with proven anti-air warfare and ballistic missile defense multi-mission capability -- is fielded on nearly 100 surface combatants worldwide.